|
Protocol
for dsDNA Quantitation using PicoGreen®
Introduction
PicoGreen
dsDNA Quantitation Reagent is an ultrasensitive fluorescent
nucleic acid stain for quantitating double-stranded
DNA (dsDNA) in solution. Detecting and quantitating
small amounts of DNA is extremely important in a wide
variety of biological applications. These include
standard molecular biology techniques, such as synthesizing
cDNA for library production and purifying DNA fragments
for subcloning, as well as diagnostic techniques,
such as quantitating DNA amplification products and
detecting DNA molecules in drug preparations.
The
most commonly used technique for measuring nucleic
acid concentration is the determination of absorbance
at 260 nm (A260) The major disadvantages of the absorbance
method are the large relative contribution of nucleotides,
single-stranded nucleic acids and proteins to the
signal, the interference caused by contaminants commonly
found in nucleic acid preparations, the inability
to distinguish between DNA and RNA, and the relative
insensitivity of the assay (an A260 of 0.1 corresponds
to a 5µg/mL dsDNA solution). Hoechst (bisbenzimide)
dyes are sensitive fluorescent nucleic acid stains
that circumvent many of these problems. The Hoechst
33258 Dye - based assay is somewhat selective for
dsDNA, does not show significant fluorescence enhancement
in the presence of proteins and allows the detection
and quantitation of DNA concentrations as low as 10
ng/mL DNA.(1)
The
Turner BioSystems TD-700 Laboratory Fluorometer used
in conjunction with Molecular Probes' PicoGreen dsDNA
Quantitation Reagent enables researchers to quantitate
as little as 25 pg/mL of dsDNA (50 pg dsDNA in a 2-mL
assay volume). This sensitivity exceeds that achieved
with the Hoechst 33258 Dye - based assay by 400-fold.
The
standard PicoGreen assay protocol is also simpler
than the Hoechst 33258 Dye method, because a single
concentration of the PicoGreen Reagent allows detection
over the full dynamic range of the assay. In order
to achieve more than two orders of magnitude in dynamic
range with Hoechst-based assays, two different dye
concentrations are recommended. In contrast, the linear
detection range of the PicoGreen assay in the TD-700
Fluorometer extends over more than four orders of
magnitude in DNA concentration - from 25 pg/mL to
1000 ng/mL - with a single dye concentration (see
figures). This linearity is maintained in the presence
of several compounds commonly found to contaminate
nucleic acid preparations, including salts, urea,
ethanol, chloroform, detergents, proteins and agarose.
The assay protocol has been developed to minimize
the fluorescence contribution of RNA and single-stranded
DNA (ssDNA). Using the PicoGreen dsDNA Quantitation
Reagent and the TD-700 Fluorometer, researchers can
quantitate dsDNA in the presence of equimolar concentrations
of ssDNA and RNA with minimal effect on the quantitation
results.
2.
Materials Required
- TD-700
Fluorometer with standard PMT and 10 mm x 10 mm square
cuvette adaptor (P/N 7000-009)
- Fluorescein
filter kit (P/N 10-086R) which includes 486 nm excitation
filter (P/N 10-105) and 510-700 emission filter (P/N
10-109R-C) and two Blue Mercury Vapor lamps (P/N 10-089).
- 10
mm x 10 mm square polystyrene disposable cuvettes
(P/N 7000-957)
- PicoGreen
dsDNA Quantitation Reagent, supplied by Molecular
Probes, Inc., Eugene, Oregon, catalog number P-7581.
A single 1-mL unit of the reagent concentrate is sufficient
for 200 assays using an assay volume of 2 mL and the
protocol described in section 3. Handling, storage
and use of the reagent should be performed in accordance
with the product information sheet supplied by Molecular
Probes, Inc.
3.
Experiment Protocol
3.1
Reagent Preparation
3.1.1
The PicoGreen dsDNA Quantitation Reagent is
supplied as a 1-mL concentrated dye solution in
anhydrous dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO). On the day of
the experiment, prepare an aqueous working solution
of the PicoGreen Reagent by making a 1:200 dilution
of the concentrated dye solution in 10 mM Tris-HCl,
1 mM EDTA, pH 7.5 (TE). To prepare enough working
solution to assay 20 samples, add 100 µL PicoGreen
dsDNA Quantitation Reagent to 20.0 mL TE. Preparing
this solution in a plastic container is recommended,
as the reagent may adsorb to glass surfaces. Protect
the working solution from light by covering it with
foil or placing it in the dark, as the PicoGreen
Reagent is susceptible to photodegradation. For
best results, this solution should be used within
a few hours of its preparation.
3.2
DNA Standard Curve
3.2.1
Prepare a 2µg/mL stock solution of dsDNA in TE.
Determine the DNA concentration on the basis of
absorbance at 260 nm (A260) in a cuvette with a
1-cm pathlength; an A260 of 0.04 corresponds to
2µg/mL dsDNA solution. Calf thymus DNA is commonly
used for a standard curve, although any purified
dsDNA preparation may be used. It is preferable
to prepare the standard curve with DNA similar to
the type being assayed; long or short linear DNA
fragments for quantitating similar-sized restriction
fragments; plasmid for quantitating plasmid DNA.
However, most linear dsDNA molecules have been found
to yield approximately equivalent signals, regardless
of fragment length. The PicoGreen assay remains
linear in the presence of several compounds that
commonly contaminate nucleic acid preparations,
although the signal intensity may be affected. Thus,
to serve as an effective control, the dsDNA solution
used to prepare the standard curve should be treated
the same way as the experimental samples and should
contain similar levels of such compounds.
To
generate a single-replicate, five-point standard
curve from 1 ng/mL to 1µg/mL, proceed to step 3.2.2.
For a low-range standard curve from 25 pg/mL to
25 ng/mL, prepare a 40-fold dilution of the 2µg/mL
DNA solution to yield a 50 ng/mL DNA stock solution
and proceed to step 3.2.5.
3.2.2
For the high-range standard curve, dilute the 2µg/mL
DNA stock solution into disposable cuvettes (or
alternatively, into plastic test tubes for transfer
to quartz cuvettes) as shown in Table 1. Then add
1.0 mL of the aqueous working solution of PicoGreen
Reagent (prepared in section 3.1) to each cuvette.
Mix well and incubate for 2 to 5 minutes at room
temperature, protected from light.
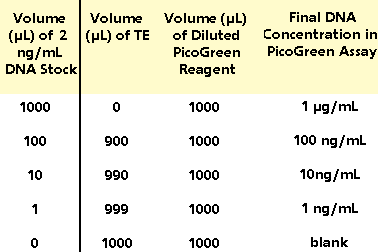
Table
1. Protocol for preparing high-range standard curve.
3.2.3
After incubation, measure the sample fluorescence
in the TD-700 Fluorometer using the fluorescein
filter kit (P/N 10-086R). Insert the most fluorescent
sample first (1µg/mL DNA) and calibrate the instrument
sensitivity as directed in the TD-700 manual (press
#2, calibrate). This procedure automatically optimizes
the instrument sensitivity to match the fluorescence
of the sample.
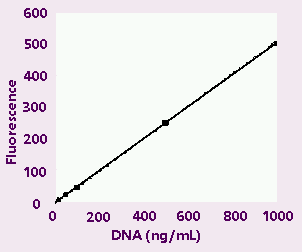
Figure
1A . High-range calibration plot.
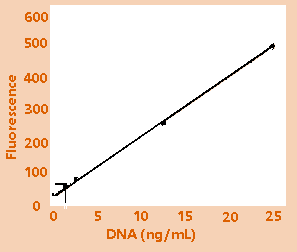
Figure
1B: Low range calibration plot.
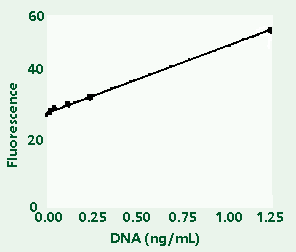
Figure
1C: Enlargement of lower left segment of Figure 1B.
Figures:
High-range (1A) and low-range (1B) calibration plots
for quantitation of calf thymus DNA on the TD-700
fluorometer. Figure 1C shows an enlargement of the
area indicated by the box in the lower left hand
corner of Figure 1B.
3.2.4
Measure the fluorescence of the remaining samples.
To equalize any photobleaching effects, insert
samples into the fluorometer for approximately equal
time periods. The fluorescence value of the
reagent blank may be subtracted from that of each
sample. Corrected or uncorrected data may be used
to generate a standard curve of fluorescence versus
DNA concentration.
3.2.5
For the low-range standard curve - from 25 pg/mL
to 25 ng/mL - dilute the 50 ng/mL DNA stock solution
(prepared in step 3.2.1) into dispoable cuvettes
(or plastic test tubes for transfer to quartz cuvettes)
as shown in Table 2. Then add 1.0 mL of the aqueous
working solution of PicoGreen Reagent (prepared
in section 3.1) to each cuvette. Mix well and incubate
for 2 to 5 minutes at room temperature, protected
from light. Insert the most fluorescent (25 ng/mL)
sample first and adjust the fluorometer sensitivity
factor (as in 3.2.3), to accommodate the lower fluorescence
signals. Measure the fluorescence of the remaining
samples. Plot a low-range standard curve (Figure
1B,C) after optionally subtracting the reagent blank
fluorescence value. A
A.
The fluorescence signal at the detection limit of
25 pg/ml dsDNA is typically about 3% above background;
however the high precision of the assay data makes
this low detection limit readily achievable in practice.
3.3
Sample Analysis
3.3.1
Dilute the experimental DNA solution in TE to a
final volume of 1.0 mL in disposable cuvettes or
test tubes. You may alter the amount of sample diluted,
provided that the final volume remains 1.0 mL. A
higher dilution of the experimental sample will
ensure that any contaminants are maximally diluted.
However, extremely small sample volumes should be
avoided because they are difficult to pipet accurately.
See section 3.4 for information on eliminating RNA
and ssDNA from the sample.
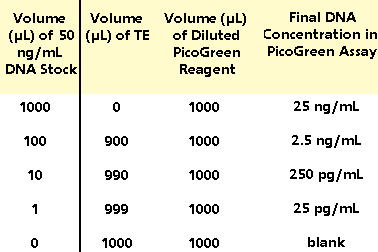
Table
2. Protocol for preparing low-range standard curve.
3.3.2
Add 1.0 mL of the aqueous working solution of the
PicoGreen Reagent (prepared in section 3.1) to each
sample. Incubate for 2 to 5 minutes at room temperature,
protected from light.
3.3.3
Measure the fluorescence of the sample using instrument
parameters that correspond to those used when generating
your standard curve (see steps 3.2.3, 3.2.4 and
3.2.5). To equalize any photobleaching effects,
insert samples into the fluorometer for approximately
equal time periods.
3.3.4
If the standard curve was plotted using blank-subtracted
data (section 3.2.4), the reagent blank fluorescence
value must also be subtracted from that of each
of the samples. Determine the DNA concentration
of the sample from the standard curves generated
in section 3.2.
3.3.5
The assay may be repeated using a different dilution
of the sample to confirm the quantitation results.
3.4
Eliminating Single-Stranded Nucleic Acids from Samples
Double-stranded
DNA can be quantitated in the presence of equimolar
concentrations of single-stranded nucleic acids
with minimal interference. A 10-fold excess of RNA
over dsDNA generally produces no more than a 10%
change in the fluorescence signal. Somewhat larger
distortions are produced by ssDNA, particularly
at low DNA concentrations (see Molecular Probes'
product information sheet MP7581 for more details).
Fluorescence due to PicoGreen Reagent binding to
RNA at high concentrations can be eliminated by
treating the sample with DNase-free RNase. (2)The
use of RNase A/RNase T1 with S1 nuclease will eliminate
all single-stranded nucleic acids and ensure that
the entire sample fluorescence is due to dsDNA.(2)
4.
References
- Anal.
Biochem. 102, 344 © 1980
- Molecular
Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, Second Edition, J. Sambrook,
E.F. Fritsch and T. Maniatis, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory
Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York © 1989.
5. Warnings and Precautions
The
PicoGreen dsDNA Quantitation Reagent is the subject
of patent applications filed by Molecular Probes,
Inc. and is not available for resale or other commercial
uses without a specific agreement from Molecular Probes,
Inc. PicoGreen is a registered trademark of Molecular
Probes, Inc.
|

