| Protocol
Using DiFMUP for Phosphatase Detection
1.
Introduction
Because
of their critical functions in eukaryotic cells, methods
for measuring protein phosphatases were established
at least as early as 1953[1]. In 1965 Fernley and Walker[2]
described the use of 4-methylumbelliferyl phosphate
(MUP) as a substrate for alkaline phosphatase. Dephosphorylation
of MUP yields a highly fluorescent and stable product:
4-methylumbelliferone (4MU).
An
improved method involves the use of 6,8-difluoro-4-methylumbelliferyl
phosphate (DiFMUP), which can assay both acid and alkaline
phosphatase activity. The hydrolysis product of DiFMUP
to DiF4MU exhibits both a lower pka (4.9 versus 7.8)
and a higher fluorescence quantum yield (0.89 versus
0.63) than the hydrolysis product of MUP. The lower
pka of its hydrolysis product makes DiFMUP a sensitive
substrate for acid phosphatases, which is not possible
with MUP because its flourescence must be measured at
alkaline pH. Furthermore, with its high quantum yield,
DiFMUP increases the sensitivity of both acid and alkaline
phosphatase measurements. Lastly, fluorination reduces
the susceptibility of the methylumbelliferone fluorophore
to photobleaching effects without significantly affecting
the extinction coefficient or excitation/emission maxima.
Combined with theTurner BioSystems TD-700 Laboratory
Fluorometer, DiFMUP enables researchers to quantitate
as little as 1.0 pg/ml alkaline phosphatase.
2.
Materials Required
- TD-700
Fluorometer with standard PMT and 10 mm × 10 mm cuvette
adaptor (P/N 7000-009)
- Near
UV Lamp (P/N 10-049)
- Excitation
Filter, 365 nm (P/N 034-0365)
- Emission
Filter, 410-610 nm (P/N 10-110R-C)
- 10
mm × 10 mm methylacrylate fluorescence cuvettes (P/N
7000-959)
- DiFMUP(6,8-difluoro-4-
methylumbelliferyl phosphate, ammonium salt)
- Sodium
Carbonate, Anhydrous (NA2CO3, MW=106.00)
- Alkaline
Phosphatase Standard
- 50mM
Tris Buffer pH 8.0.
- Bovine
Serum Albumin (BSA)
3.
Experiment Protocol
3.1
Reagent Preparation
DiFMUP
Substrate Stock Solution, 1mg/mL. Dissolve 5.0 mg
DiFMUP into 5.0 mL 50 mM Tris/0.1% BSA buffer, pH
8.0. Make up fresh daily.
NOTE: DiFMUP spontaneously hydrolyzes in
aqueous solution. It should be stored in its solid
form and made up just prior to use.
DiFMUP
Substrate Working Solution, 10µg/mL. Dilute 300
µL DiFMUP Substrate Stock Solution into 30 mL 50mM
Tris/0.1% BSA Buffer, pH 8.0. Make up fresh daily.
Alkaline
Phosphatase Stock Solution, 1 mg/mL. (Biozyme calf-intestine
alkaline phosphatase, 15.42 mg/ml). Dilute 100 µl
alkaline phosphatase into 1.4 mL 50mM Tris/0.1%
BSA buffer, pH 8.0.
Alkaline
Phosphatase Standard Solution, 500 µg/mL. Dilute
1ml AP Stock Solution with 1mL Tris/0.1% BSA buffer.
Carbonate
Stop Buffer(0.20M). Dissolve 21.2g Sodium Carbonate,
anhydrous into 1000mL DI water.
3.2.
Instrument Set-Up
- Turn
on the TD-700 Fluorometer. Allow it to warm up
for 10 minutes (600 seconds).
- Ensure
the lamp is installed by checking that the small
window in the back panel is lit or by removing
the filter cylinder and observing the lamp emission
in the sample chamber.
- Ensure
that the excitation filter, P/N 034-0365, is installed
in the position marked EX and the emission filter,
P/N 10-110R-C, is installed in the corresponding
position marked EM in the filter cylinder.
3.3.
Instrument Calibration
- Calibrate
the instrument with the 20µg/mL AP standard solution
listed in Table 1 according to the TD-700 Operating
Manual, page 21. Set the sample setting to 900.
Choose [9] or [No] when prompted to subtract blank.
3.4
Alkaline Phosphatase Standard Curve
- To
generate a single-replicate, six- point standard
curve from 20 µg/mL to 1 µg/mL, add 0.5 mL 10µg/mL
DiFMUP Working Solution to each of 6 cuvettes.
- Add
an aliquot of 500 µg/mL AP Standard Solution to
a cuvette and incubate the mixture for two minutes
at room temperature.
- Add
Carbonate Stop Buffer (0.20M) to the cuvette to
make a total volume of 2.5 mL. Mix.
- Take
a fluorescence measurement immediately.
- Repeat
steps 3.4.1 through 3.4.4 with each standard (Table
1).
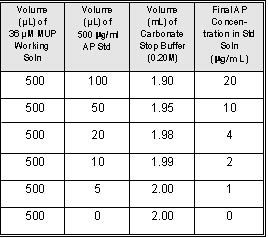
Table 1
Generate
a standard curve of fluorescence versus alkaline
phosphatase concentration (Figure 1).
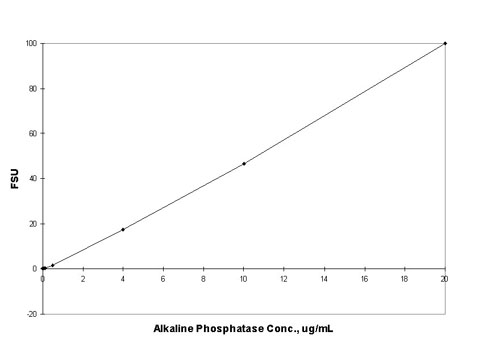
Figure 1: Fluorescence of DiF4MU from reaction
of Alkaline Phosphatase with 10 µg/mL DiFMUP and quenched
with 100mM NaCO3. The fluorescence value of the reagent
blank may be subtracted from that of each sample.
3.5
Alkaline Phosphatase Samples
- Add
0.5 mL 10µg/mL DiFMUP Working Solution to each
sample cuvette.
- Add
100 µL of sample to a cuvette, invert to mix.
- Incubate
the mixture for two minutes at room temperature.
- Add
1.9 mL Sodium Carbonate Solution to the cuvette
to make a total volume of 2.5 mL. Mix.
- Take
a fluorescence measurement immediately.
- Repeat
steps 3.5.1 through 3.5.5 with each sample.
- Calculate
the amount of alkaline phosphatase from the fluorescence
measurement and the linear equation determined
from the AP standard concentration vs. fluorescence,
step 3.4.6.
4.
References
1:
Brandenberger, H., and Hanson, R., Spectrophotometeric
Determination of Acid and Alkaline Phosphatases, Helv.
Chim. Acta, 36, 900, 1953.
2:
Fernley, H. N. and Walker, P. G., Kinetic Behaviour
of Calf-Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase with 4-Methylumbelliferyl
Phosphate, Biochem. J., 97, 95, 1965.
|

